Predictive tools have been used for decades by petroleum engineers and geologists to find and recover oil and gas resources. As technology advances, our understanding of subsurface geology sharpens and we often have to re-think our strategies for producing these valuable energy resources. Most of the easy to find and recover oil has been produced. The remaining oil is located in more complex environments, making it more difficult to find and more expensive to extract.
Luff Exploration has developed the Intelligent Computing System (ICS) as a tool to assist decision makers in selection of optimal drill-site locations and to reduce risks associated with drilling operations. ICS is a package of software tools and a reservoir characterization strategy to better access reservoir limits, producibility and favorable depositional setting. ICS uses clustering, artificial neural networks, and classical regression methods to combine seismic, geologic and engineering data for predictions of reservoir potential.
Project Results
Intelligent Computing System software has been developed and proven for predictive modeling in the Red River formation in the Williston Basin.
Benefits
The project has developed user friendly software for neural networks solving of complex seismic and reservoir characterization problems. ICS software provides a means to correlate data from well logs, and production data, and integrate it with seismic data to make accurate stratigraphic predictions necessary for successful drilling and completions. As of July 2003, field trials conducted in the Red River formation in the Williston Basin have increased proved oil reserves by 3.25 MMbbl, and increased oil production over 2.6 M bbl/day. The horizontal wells are expected to produce over 1 MMbbl of incremental oil by 2005.
Project Summary
- The ICS software developed for integrated reservoir characterization and risk assessment for petroleum exploration.
- A software toolkit was designed to correlate relationships between seismic information and well data.
- ICS software tools are implemented in MATLAB™, an integration and visualization program. ICS is designed to run on Windows without purchase of MATLAB™.
- ICS toolkit tested on seismic and well data from six 3-D seismic surveys and wells within survey boundaries in the Williston Basin.
- Generic approach reservoir characterization modules that can be used: depositional setting, structure and growth history, seismic pseudo-reservoir parameters (variations in thickness and porosity), fluid saturation, structure and stratigraphic entrapment, and combining and weighting characterization parameters.
- The test site at Amor South field in the Red River formation has undergone complex depositional processes and tectonic growth since the time of deposition (450 million years ago) resulting in difficult to interpret structure and stratigraphy.
- Seismic attributes were transformed to reservoir attributes and finally to production attributes for predictive modeling of Amor South field.
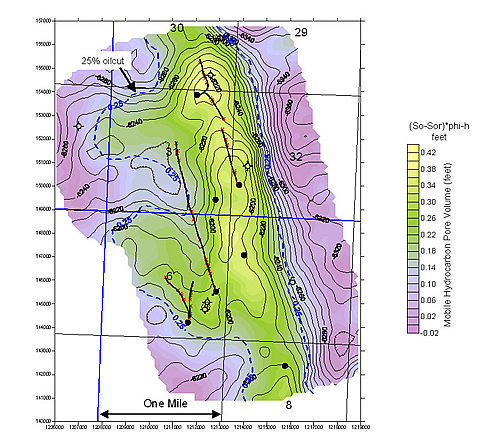
- Original mobile-oil-in-place for Red River Zone B at Amor South field was calculated at 3.1 MMbbl using seismic attributes.
- Luff Exploration developed the ICS software to use reservoir characterization data to make predictions of where to drill and recomplete wells to optimize oil production.
Several software tools within the ICS package are used to transform seismic attributes to reservoir characteristics such as thickness, porosity, permeability, and entrapment pressure. Data from wells within seismic surveys are used as training control to transform seismic attributes to conventional reservoir attributes. Seismic-transformed reservoir characteristics can be combined with well production data from a lager database through a neural network solver to describe oil-water contacts, oil-cut and producibility.
The ICS software has been successful in exploitation field trials of the Red River B Zone in the Williston Basin at South Amor field, North Dakota. The Red River B Zone is a thin dolomite reservoir with an average thickness of 7 feet and an average depth of 9,000 ft. With a thickness ranging from only 4 to 15 feet, change in reservoir development is practically invisible to visual observation of seismic waveform character. The ICS software uses well logs, drill-stem tests and production data from several hundred wells in both the Red River B and C zones to correlate with the seismic data to overcome the resolution problems. The neural network solver was able to contour the interval revealing a tilted oil-water contact and predicting the oil-cut.
Application of ICS technology significantly reduced the risks associated in drilling horizontal wells in the Red River formation, and paid off in terms of reduced exploitation costs, increased reserves discovered and increased production. Predictions from ICS were used to re-enter and drill horizontal laterals in 16 vertical wells. These vertical wells were producing an average of 20 bbl/day each. Following completion as horizontal wells the initial production was 200-300 bbl/day/well. During the 24 months following the horizontal completions the 16 wells have produced an average of 43,300 bbl/month.