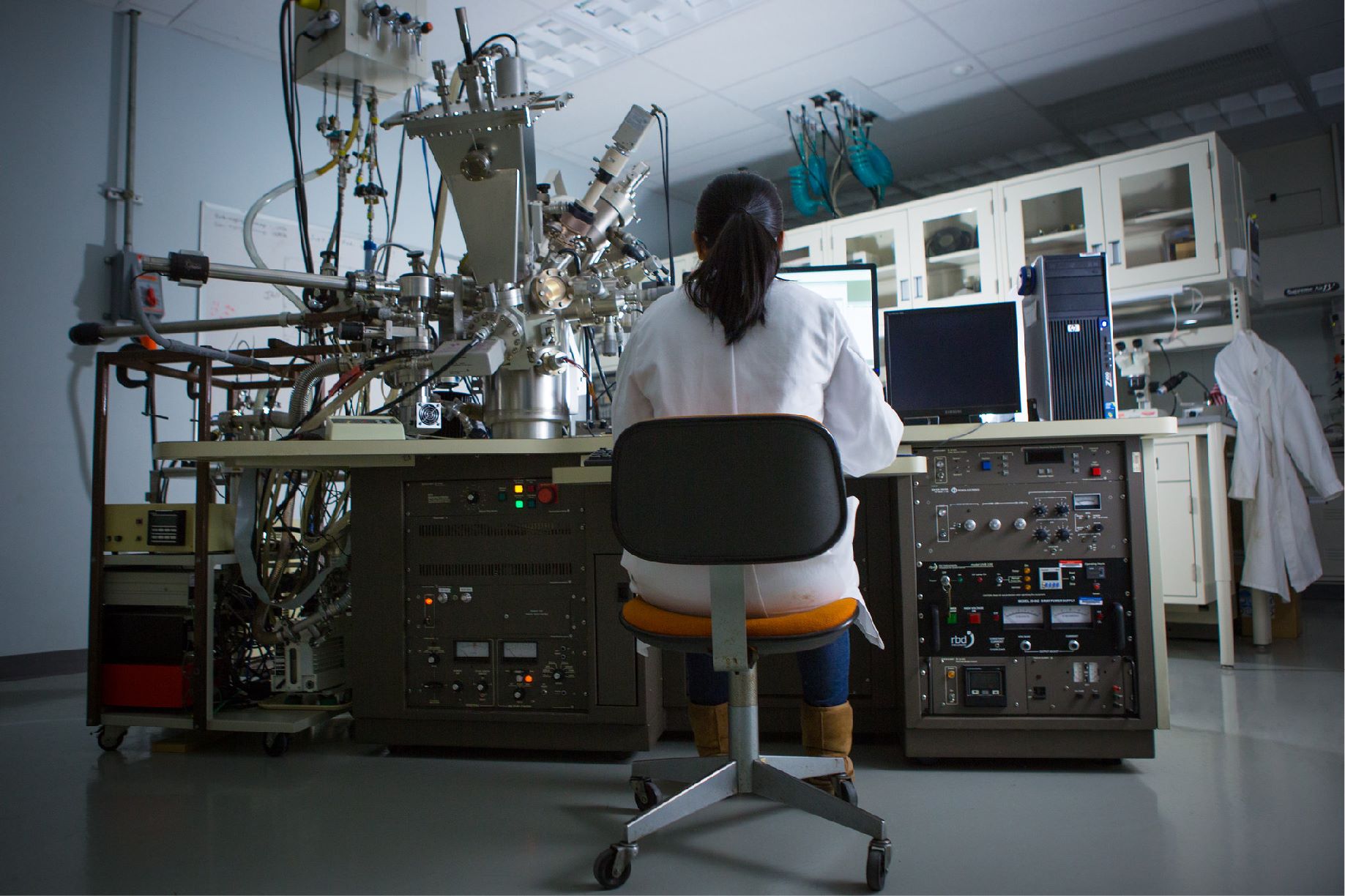
The eXtremeMAT team will provide a webinar presentation Thursday, Jan. 21 to American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) committee members, providing information and feedback including how eXtremeMAT’s work may impact ASME standards in the future.
The presentation, “Accelerating the Development of Extreme Environment Materials,” will summarize the team’s recent advances to develop physics-based models to predict long-term alloy performance in harsh service conditions and to detail a strategy proposed by eXtremeMAT for using these models to accelerate the qualification of alloys.
Initiated in 2018, the eXtremeMAT consortium, led by NETL with support from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and its Office of Fossil Energy, leverages the unparalleled materials science and engineering expertise and capabilities available within the DOE national laboratory complex to accelerate development of affordable and durable materials for extreme environment service. eXtremeMAT aims to develop, validate and integrate advanced models to predict how microstructure and composition of certain steels affect alloys designed for harsh service environments.
About
News and Events
Research and Programs
Carbon Management Point Source Carbon Capture Carbon Dioxide Removal Carbon Dioxide Conversion Carbon Transport & Storage Hydrogen with Carbon Management
Resource Sustainability Methane Mitigation Technologies Minerals Sustainability Natural Gas Decarbonization and Hydrogen Technologies Advanced Remediation Technologies Energy Asset Transformation
Key Lab Initiatives Advanced Alloys Signature Center (AASC) Science-based Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Institute (SAMI) Center for Microwave Chemistry (CMC) Center for Sustainable Fuels and Chemicals (CSFC)
Energy Technology Development Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Battery Workforce Initiative Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response Office of ElectricityGrid Resilience
Business
Library
Explore our Library

Approved Categorical Exclusions Environmental Assessments Environmental Impact Statements Oil and Gas Projects Summaries NETL Fact Sheets NETL Newsletters Publication Search Energy Data Exchange (EDX) FECM External R&D Final Technical Reports Summary Information for External R&D Awards Technical Reports Series (TRS) Peer Review Reports Interagency Working Group Initial Report
- Research and Programs
- Carbon Management
- Core Competencies
- Resource Sustainability
- University Training & Research
- Key Lab Initiatives
- Energy Technology Development
- Featured Infrastructure
- Methane Emissions Reduction Program
-
- Business
- Technology Transfer
-
- Library
- Energy Analysis
-
- About
- News and Events
- Education